
Precipitation - UK / US noun 1) science rain, snow, hail etc 2) chemistry the process by which a solid substance separates, or is separated from, a liquid it is in 3) formal a way of behaving in which someone does something too… … English dictionary 3》 archaic the fact or quality of acting precipitately … English new terms dictionary 2》 rain, snow, sleet, or hail that falls to or condenses on the ground. Precipitation - noun 1》 Chemistry the action or process of precipitating a substance from a solution. rain, snow, hail, etc.) … English contemporary dictionary haste, rush, hurry separation of a solid from a solution (Chemistry) condensed moisture that falls from the sky (i.e. unwise or… … Australian-English dictionary a hastening or hurrying in movement, procedure, or action. Precipitation - /prəsɪpəˈteɪʃən / (say pruhsipuh tayshuhn) noun 1. 3) archaic sudden and unthinking action … English terms dictionary 2) Chemistry the action or process of precipitating.

Precipitation - ► NOUN 1) rain, snow, sleet, or hail that falls to or condenses on the ground.
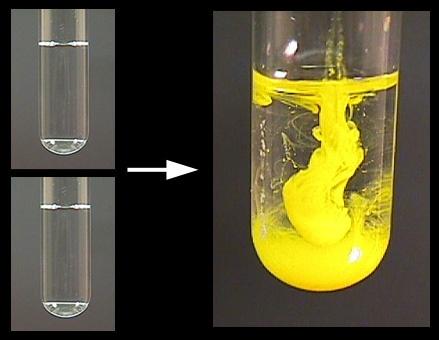
Precipitation - may refer to: * Precipitation (meteorology), rain, sleet, hail, snow and other forms of water falling from the sky * Precipitation (chemistry), the condensation of a solid from a solution during a chemical reaction * Precipitation (horse), a… … Wikipedia In metallurgy, precipitation from a solid solution is also a useful way to strengthen alloys this process is known as solid solution strengthening. Precipitation is also useful in purifying products: crude bmim-Cl is taken up in acetonitrile, and dropped into ethyl acetate, where it precipitates. An example would be the synthesis of chromic tetraphenylporphyrin chloride: water is added to the DMF reaction solution, and the product precipitates. Thereafter, the precipitate may easily be separated by filtration, decanting, or centrifugation). Precipitation may also occur when an antisolvent (a solvent in which the product is insoluble) is added, drastically reducing the solubility of the desired product. By cooling the reaction mixture to room temperature, crystals of the porphyrin precipitate, and are collected by filtration: An example of this would be the synthesis of porphyrins in refluxing propionic acid. Thus, it precipitates as it is formed, preferably forming pure crystals. Ideally, the product of the reaction is insoluble in the reaction solvent. Precipitation is also useful to isolate the products of a reaction during workup. Precipitation reactions can be used for making pigments, removing salts from water in water treatment, and in classical qualitative inorganic analysis. If this energy is not available, and no suitable nucleation surface is available, supersaturation occurs.Ĭrystals of meso-tetratolylporphyrin from refluxing propanoic acid precipitate on cooling The creation of a hypothetical solid particle includes the formation of an interface, which requires some energy based on the relative surface energy of the solid and the solution. Īn important stage of the precipitation process is the onset of nucleation. Precipitation in solids is routinely used to synthesize nanoclusters. rapid quenching or ion implantation, and the temperature is high enough that diffusion can lead to segregation into precipitates. In solids, precipitation occurs if the concentration of one solid is above the solubility limit in the host solid, due to e.g. With soluble substances, precipitation is accelerated once the solution becomes supersaturated. During chemical reactions, precipitation may also occur particularly if an insoluble substance is introduced into a solution and the density happens to be greater (otherwise the precipitate would float or form a suspension). Natural methods of precipitate include settling or sedimentation, where a solid forms over a period of time due to ambient forces like gravity or centrifugation. Powders derived from precipitation have also historically been known as flowers. The liquid remaining above the solid is in either case called the supernate or supernatant. When the reaction occurs in a liquid, the solid formed is called the precipitate, or when compacted by a centrifuge, a pellet. Precipitation is the formation of a solid in a solution or inside another solid during a chemical reaction or by diffusion in a solid.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
